Table of Contents
ToggleDietary fiber is a vital component for maintaining optimal health, often celebrated for its ability to aid in digestion, support heart wellness, and assist in weight management. Vegetables are particularly praised for being robust sources of fiber and pivotal nutrients, making them an integral part of a balanced diet. This article delves into the benefits and options of high-fiber vegetables, enabling individuals to make informed dietary choices.
Daily Fiber Recommendations
General Guidelines
Health experts prescribe a daily fiber intake of about 14 grams for every 1,000 calories consumed. This guideline serves as a reference point, varying slightly depending on age and dietary needs. Each demographic has specific recommendations to ensure their dietary fiber requirements are met adequately.
Importance of Meeting Daily Fiber Goals
Achieving daily fiber goals is paramount for optimizing digestion and diminishing the risk of chronic illnesses. A diet rich in fiber is associated with numerous health advantages, including fostering regular bowel movements and curtailing the likelihood of experiencing digestive issues.
High-Fiber Vegetable Options
Leafy Greens
- Kale: Contains 4.7 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, making it a significant source of daily fiber intake.
- Spinach: Offers 4.3 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, adding valuable nutrient-rich variety.
- Collard Greens: These greens provide 4 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, an appealing addition to meals.
- Swiss Chard: Another nutritive option delivering 4 grams of fiber per one cup cooked.
Cruciferous Vegetables
- Broccoli: With 5.2 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, it’s a popular choice for fiber-conscious diets.
- Brussels Sprouts: Feature 6.4 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, enhancing its nutritional importance.
- Cauliflower: Another noteworthy option, offering 4.9 grams of fiber per one cup cooked.
Root and Bulb Vegetables
- Artichoke: Stands out with an impressive 9.6 grams of fiber per one cup cooked.
- Sweet Potato: Delivers 6.3 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, doubling as a sweet and savory option.
- Carrots: Provides 4.8 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, ideal for multiple culinary uses.
Other High-Fiber Vegetables
- Avocado: Offers a notable 5.0 grams of fiber per one-half cup, perfect for spreads and salads.
- Potatoes: At least 3 grams of fiber per medium potato, skin included, making it a staple in fiber-rich diets.
- Okra: Delivers 4 grams of fiber per one cup cooked, adding diversity to vegetable choices.
Health Benefits of High-Fiber Vegetables
Digestive Health
Consuming fiber-rich vegetables can prevent constipation by enhancing stool bulk and improving water absorption, facilitating smoother digestion. Additionally, maintaining a diet high in fiber is linked to a reduced risk of hemorrhoids and diverticular diseases, bolstering overall digestive health.
Heart Health
Soluble fibers found in vegetables are instrumental in lowering LDL cholesterol levels, thereby supporting cardiovascular health. Furthermore, fiber helps reduce blood pressure and inflammation, contributing to a healthier heart and circulatory system.
Blood Sugar Control
High-fiber diets play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels by reducing spikes, offering a steadier metabolic rate, and aiding individuals with sugar-sensitive conditions like diabetes.
Weight Management
Foods high in fiber tend to increase satiety, helping people feel full longer, which is beneficial in weight management strategies and reducing overeating tendencies.
Incorporating High-Fiber Vegetables into Your Diet
Meal Ideas
- Salads and Soups: Enhance your meals by incorporating high-fiber vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and artichokes.
- Roasted Vegetables: Transform Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and sweet potatoes into delicious, nutrient-rich sides.
- Stir-Fries and Grilled Vegetables: Explore diverse flavors with a variety of high-fiber vegetables in your culinary creations.
Snacking
- Raw or Steamed: Enjoy the fresh flavors of raw or steamed vegetables as convenient and healthy snacks.
- Dips and Spreads: Incorporate high-fiber options like avocado to elevate dips and spreads.
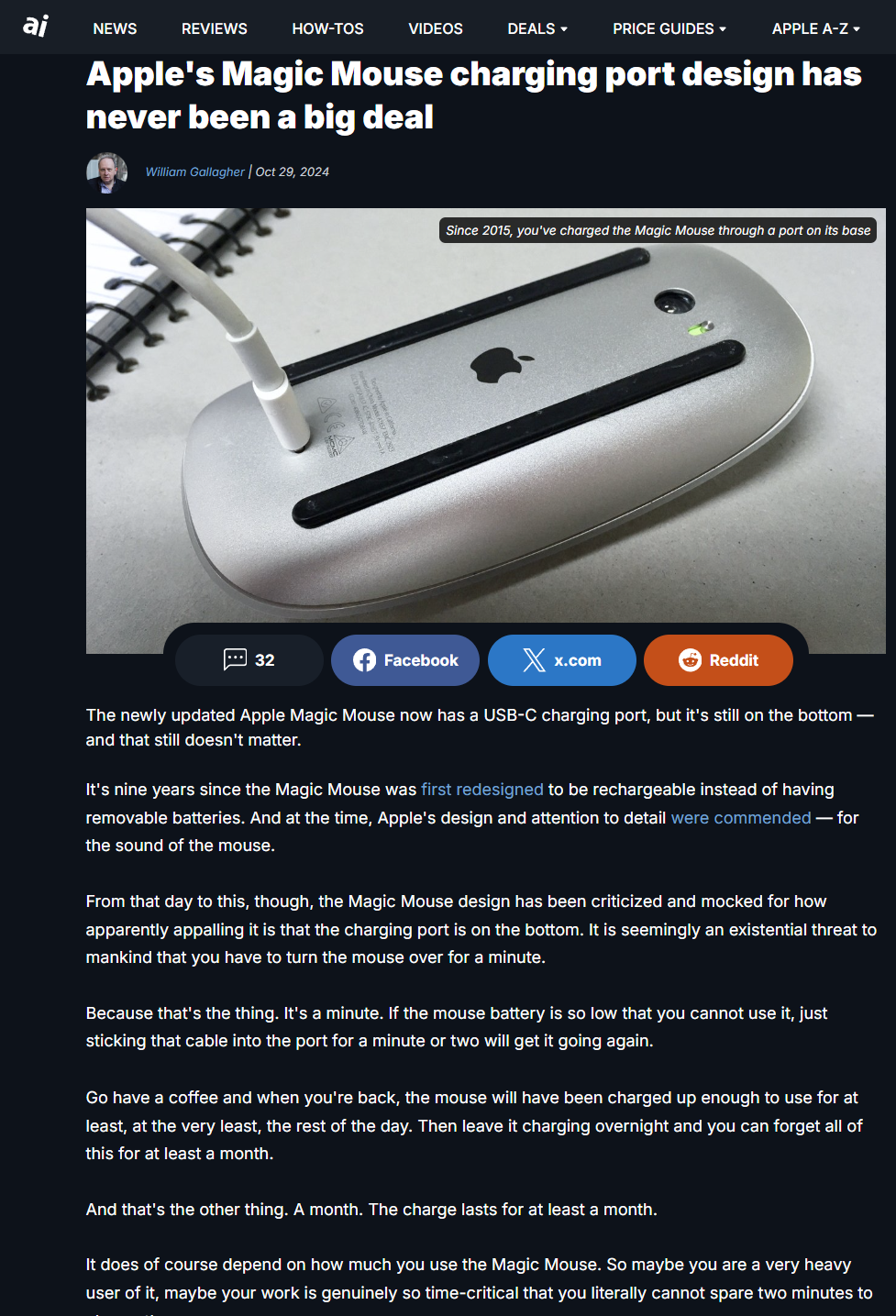
In conclusion, high-fiber vegetables are essential for anyone looking to harness their diet for improved health outcomes. Not only do they support digestion, but they also contribute to heart health, blood sugar control, and effective weight management. Incorporating a variety of these nutrient-rich vegetables will ensure a balanced and wholesome diet.
For more articles and updates on how to maintain a healthy diet, continue following FROZENLEAVES NEWS.
Source: Nutrition Journal
“`